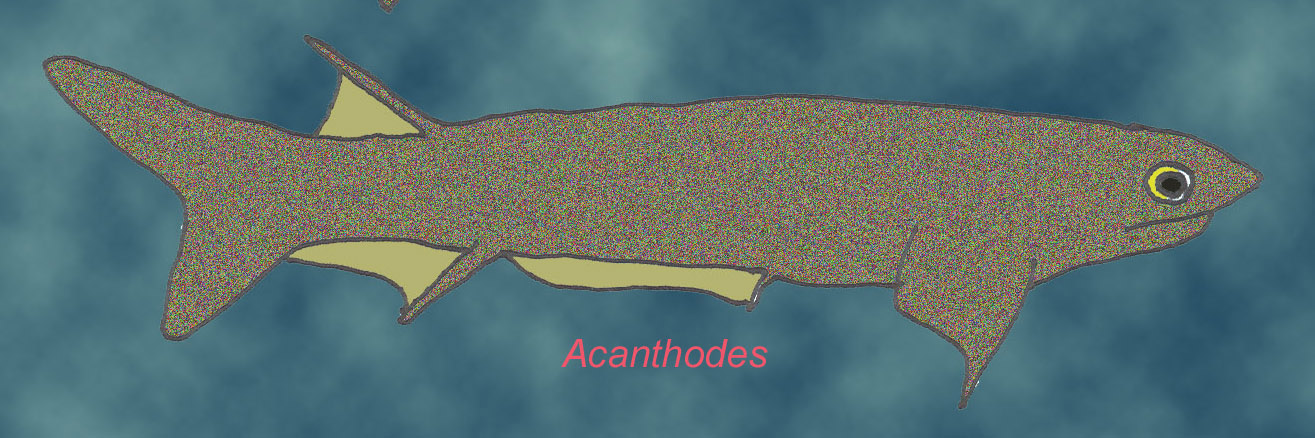
Overview of Acanthodians
Definition and Characteristics of Acanthodians
Acanthodians, often referred to as "spiny sharks," are a group of primitive jawed fish that flourished during the Paleozoic era. They are characterized by their unique features, which include:
- Spiny Fins: Acanthodians display prominent spines in their dorsal fins, giving them their nickname.
- Streamlined Bodies: Their sleek anatomy suggests they were agile swimmers, adept at navigating in the water.
- Small Size: Most Acanthodians were relatively small, averaging a few inches in length.
These characteristics set Acanthodians apart from other early vertebrates, providing insights into the diversity of marine life during their time.
Evolutionary History of Acanthodians
The evolutionary history of Acanthodians is fascinating and complex. They first appeared in the Silurian period, roughly 440 million years ago, and thrived until their decline in the late Permian period. Key points to note include:
- Diversity: At their peak, Acanthodians exhibited remarkable variety, with over 30 known families evolving, each adapted to different ecological niches.
- Ancestral Importance: Acanthodians are considered significant in understanding the transition from jawless to jawed vertebrates, bridging gaps in early fish evolution.
Their presence underscores a crucial chapter in the story of life's evolution on Earth, showcasing the adaptability and diversity of early vertebrates. The more researchers learn about Acanthodians, the more they appreciate their role in the lineage leading to contemporary fish species.
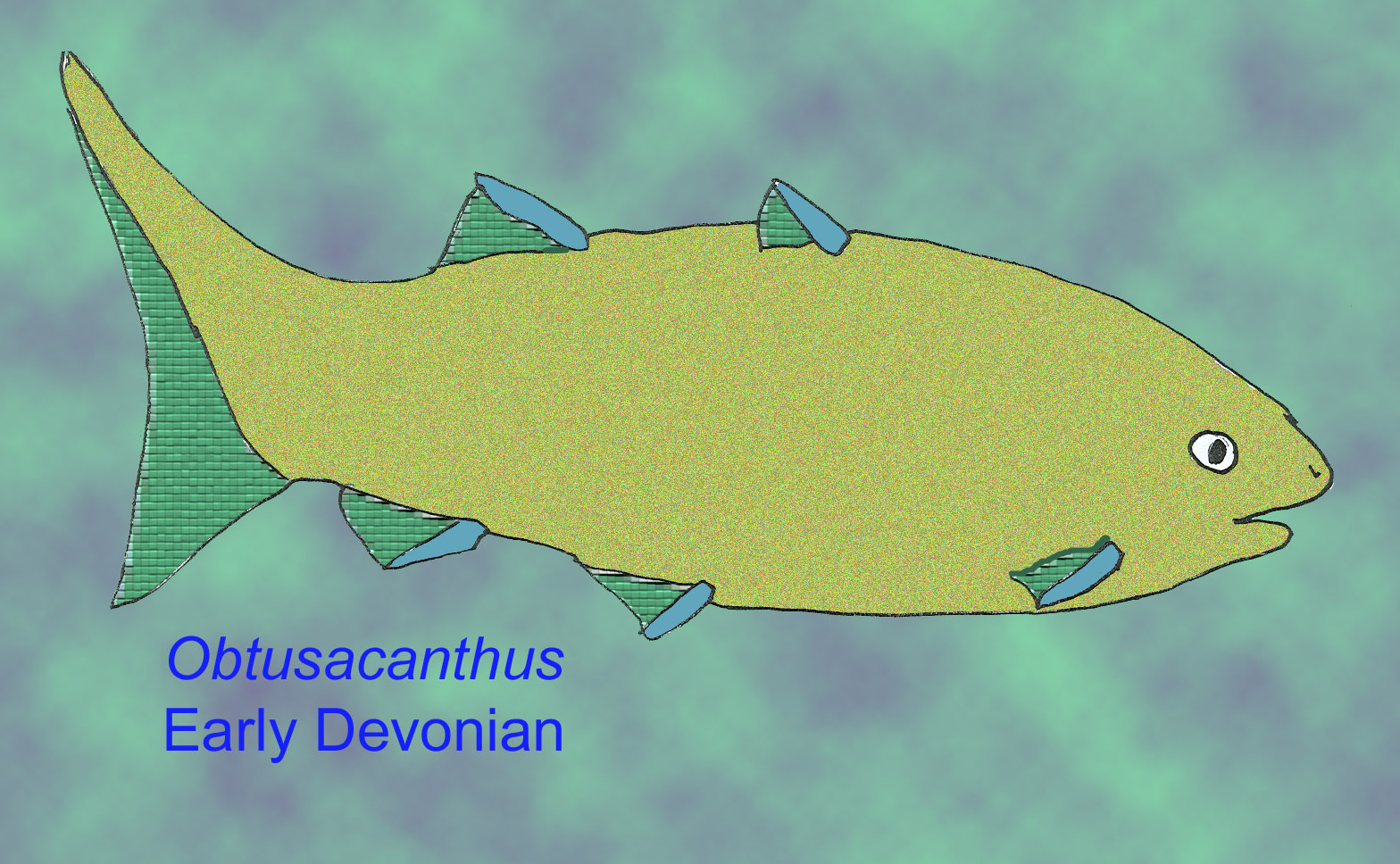
Classification of Acanthodians
Different Families of Acanthodians
Acanthodians are not a single entity; they comprise various families, each showcasing unique traits that highlight their diversity. Some notable families include:
- Acanthodes: Perhaps the most well-known, characterized by slender bodies and multiple dorsal spines.
- Ischnacanthidae: Noted for their distinctive jaw structures and broad, flattened bodies.
- Mesacanthidae: Recognized for their robust build and a suite of adaptations that hint at a predatory lifestyle.
Each family evolved to occupy specific ecological niches, underlining the adaptability of Acanthodians during their prominence in prehistoric waters.
Distribution of Acanthodians in Fossil Record
The fossil record of Acanthodians is rich and geographically widespread, providing crucial insights into their historical presence. Key highlights include:
- Global Reach: Fossils have been discovered across every continent, from North America to Europe and even parts of Asia and Africa.
- Preservation: The characteristics of their skeletal remains allow paleontologists to piece together their anatomy and behavioral adaptations.
These fossils serve as vital clues, allowing researchers to unravel the complex web of early vertebrate evolution and the environments in which these fascinating creatures thrived. Understanding their classification aids in painting a fuller picture of life millions of years ago.
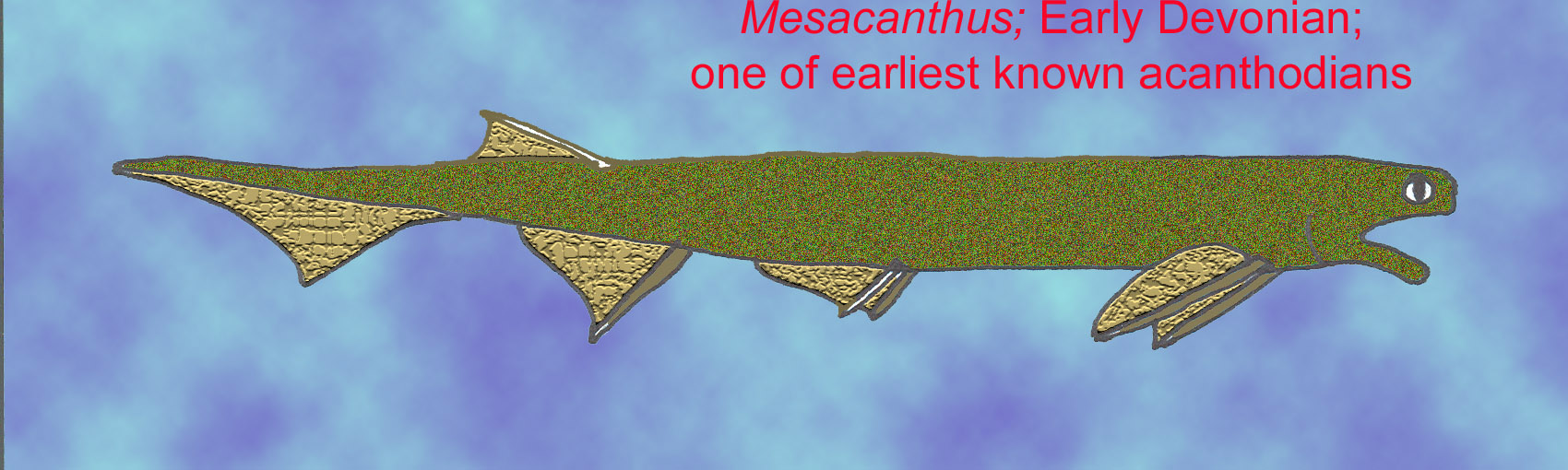

Anatomy and Behavior of Acanthodians
Physical Features of Acanthodians
Diving deeper into the anatomy of Acanthodians reveals a blend of features tailored for their aquatic lifestyles. Their physical attributes include:
- Streamlined Bodies: These fish possessed elongated, streamlined shapes that facilitated swift movement through water.
- Distinctive Spines: Acanthodians are famously adorned with prominent spines along their dorsal fins, which likely added stability and defense against predators.
- Skeletal Structure: Their skeletons were primarily cartilaginous, making them lighter and more agile compared to their bony counterparts.
Such features underscore their adaptability and prowess in prehistoric marine environments.
Feeding Habits and Adaptations
Feeding habits of Acanthodians were as diverse as their physical characteristics. Depending on their size and morphology, they exhibited various strategies:
- Carnivorous Diet: Many Acanthodians were predatory, preying on smaller fish and invertebrates. Their sharp teeth aided in capturing slippery prey.
- Filter Feeding: Some species adapted a more passive approach, utilizing gill rakers to filter plankton from the water.
These feeding adaptations highlight how Acanthodians successfully navigated their ecosystems, demonstrating their evolutionary ingenuity in a time when the oceans were teeming with life. Witnessing their adaptations enriches our understanding of early vertebrate dietary strategies.
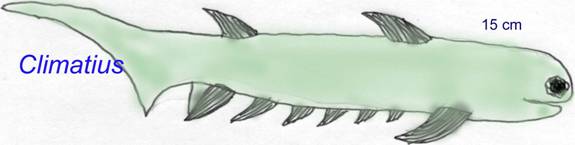
Significance of Acanthodians in Paleontology
Role of Acanthodians in Ecosystems
Acanthodians played a crucial role in prehistoric marine ecosystems, acting as both predators and prey. Their presence contributed to the biodiversity of ancient oceans. Key points about their ecological role include:
- Predatory Functions: As agile hunters, they helped regulate populations of smaller fish and invertebrates.
- Food Source: They served as a vital food source for larger marine animals, highlighting their position in the food web.
By examining their role, researchers gain insights into the dynamics of ancient ecosystems, emphasizing the interconnectedness of marine life.
Contributions to Understanding Early Vertebrate Evolution
Studying Acanthodians offers significant contributions to the understanding of early vertebrate evolution. These fish reveal critical evolutionary transitions, such as:
- Jaw Development: Acanthodians represent an important step in the evolution of jaws, showcasing the early adaptations that led to more advanced fish.
- Morphological Diversity: Their varied anatomical features highlight the evolutionary experimentation that occurred during the Devonian period.
Through Acanthodians, paleontologists can piece together the intricate puzzle of vertebrate lineage, shedding light on how modern fish evolved from these fascinating ancient creatures. Their legacy continues to shape our understanding of evolutionary biology.

Extinction of Acanthodians
Factors Leading to the Extinction of Acanthodians
The extinction of Acanthodians is a complex topic influenced by multiple factors. As they thrived in prehistoric oceans, several challenges began to emerge:
- Environmental Changes: The late Permian period witnessed significant shifts, including changes in ocean temperatures and chemistry that impacted marine habitats.
- Competition: Increasing competition from more advanced bony fishes and evolving predators may have outcompeted Acanthodians.
- Mass Extinctions: The Permian-Triassic extinction event, one of Earth's most catastrophic extinctions, played a pivotal role in eliminating many marine species, including Acanthodians.
These factors combined led to their eventual decline by the end of the Permian period.
Legacy of Acanthodians in Modern Fishes
Despite their extinction, Acanthodians leave a lasting legacy in the lineage of modern fish. Their unique adaptations and evolutionary significance paved the way for future marine life. Points to consider include:
- Evolutionary Ancestors: They serve as crucial ancestral links that help trace the lineage of bony fishes and cartilaginous sharks.
- Anatomical Insights: By studying their unique physical features, scientists gain insights that help explain the diversity and adaptability of current fish species.
The story of Acanthodians highlights the evolution of life in the oceans, reminding us of the intricate connections that bind today’s fish to their ancient predecessors. Their legacy continues to inspire and inform scientific research in paleontology and evolutionary biology.
